84. 柱状图中最大的矩形 #
链接 #
题目 #
给定 n 个非负整数,用来表示柱状图中各个柱子的高度。每个柱子彼此相邻,且宽度为 1 。
求在该柱状图中,能够勾勒出来的矩形的最大面积。
示例 1:
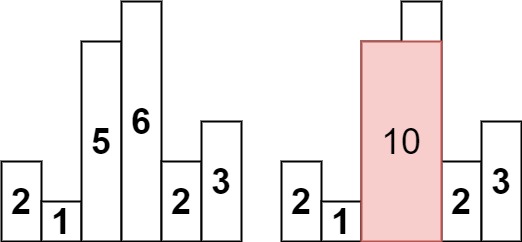
输入:heights = [2,1,5,6,2,3] 输出:10 解释:最大的矩形为图中红色区域,面积为 10
示例 2:
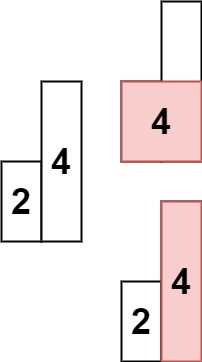
输入: heights = [2,4] 输出: 4
提示:
1 <= heights.length <=1050 <= heights[i] <= 104
解答 #
代码 #
def largestRectangleArea(heights):
# 在heights数组的开头和结尾分别添加高度为0的柱子,
# 以简化代码逻辑,处理边界情况
heights = [0] + heights + [0]
max_area = 0
stack = [] # 单调栈,存储柱子的索引
for i, h in enumerate(heights):
# 当前柱子的高度小于栈顶柱子的高度时,计算栈顶柱子的最大面积
while stack and heights[stack[-1]] > h:
height = heights[stack.pop()]
width = i - stack[-1] - 1
max_area = max(max_area, height * width)
stack.append(i)
return max_area
思路详解 #
以 1 2 5 1 6 3 为例。
假设新元素入栈不破坏单调性,那么就让它的坐标入栈。
刚开始我们处于 i = 0 的位置。发现三个连续单增项,让其下标入栈。
因此得到下标 0 1 2对应 1 2 5,这时候再进入下一个元素—— 1 会导致单调性破坏。
因此开始出栈。
首先 5 出栈,其面积结算为 5。(面积怎么算的:用 i 作为右边界,用栈顶元素 stk.top()+1 作为左边界,我们会发现面积夹在中间,如下图红色所示。宽度为右边界减去左边界+1,即 i - stk.top() - 1。高度则为 height[outidx],即 5.)
然后栈顶变成 2, 还是大于将来的 1. 因此开始出栈,2 出栈,其面积结算为4
我们要求严格单增,所以 1 也要出栈。结算 4 面积。
之后是一波增长红利期,1、6 的下标入栈。
遇到了 3,无法增长,开始结算。6 被结算得 6.
此时 3 可以入队了。同时遇到空气墙。
结算 3, 得到 6
最后一步 栈空了,此时应当以 0 作为左边界(否则遇到 {2 1 2} 这种输入就要被坑)结算得到 6.
在上述结算面积中,最大的是 6.
上述过程的日志如下:
push 0(1)
push 1(2)
push 2(5)
pop 2(5)
width = 1
area = 5
pop 1(2)
width = 2
area = 4
pop 0(1)
width = 3
area = 3
push 3(1)
push 4(6)
pop 4(6)
width = 1
area = 6
push 5(3)
pop 5(3)
width = 2
area = 6
pop 3(1)
width = 6
area = 6
6
注意事项 #
- 向
heights末尾推个 0, 这样能促使末尾增长序列的结算。 - 注意条件是
heights[stk.top()] < heights[i]很容易漏写成stk.top() < heights[i]非常难调试 - 当栈空了的时候,应当以 0 作为左边界。
- 栈空了,程序也不一定结束。
- 注意循环条件 是
i < n或!stack.empty()
下面是两种带详细输出的写法,如果看不懂别人的解析,很正常,建议结合输出理解。
class Solution {
public:
int largestRectangleArea(vector<int>& heights) {
int n = static_cast<int>(heights.size()), maxarea = 0;
heights.push_back(0);
stack<int> stk;
int i = 0;
do {
while (stk.empty() || heights[stk.top()] < heights[i]) {
stk.push(i);
std::cout << "push " << i << "(" << heights[i] << ")" << std::endl;
i++;
}
auto outidx = stk.top();
stk.pop();
auto out = heights[outidx];
std::cout << "pop " << outidx << "(" << heights[outidx] << ")"
<< std::endl;
auto width = stk.empty() ? i : i - stk.top() - 1;
printf("width = %d\n", width);
auto area = width * out;
std::cout << "area = " << area << std::endl;
maxarea = max(area, maxarea);
std::cout << std::endl;
} while (i < n || !stk.empty());
return maxarea;
}
int largestRectangleArea2(vector<int>& heights) {
stack<int> stk;
int maxArea = 0;
heights.push_back(0);
for (int i = 0; i < heights.size(); i++) {
while (!stk.empty() && heights[i] < heights[stk.top()]) {
auto height = heights[stk.top()];
std::cout << "pop " << stk.top() << "(" << height << ")" << std::endl;
stk.pop();
int width = stk.empty() ? i : i - stk.top() - 1;
printf("width = %d\n", width);
printf("area = %d\n", height * width);
std::cout << std::endl;
maxArea = max(maxArea, height * width);
}
stk.push(i);
std::cout << "push " << i << "(" << heights[i] << ")" << std::endl;
}
return maxArea;
}
};